
Amidst the vast expanse of African landscapes lies a transformative approach to agriculture – Regenerative Agriculture. A movement gaining momentum globally, it holds the promise of not just sustainable yields but also healing and rejuvenating the very earth that sustains us. In this illuminating guide, we delve into the profound benefits of embracing Regenerative Agriculture in Africa. We explore how it can revitalize ecosystems, bolster farmer livelihoods, and safeguard the future. Moreover, we provide practical insights into the practices that farmers can start with, ushering in a new era of sustainable agriculture that captivates both hearts and harvests.
Unveiling the Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture in Africa
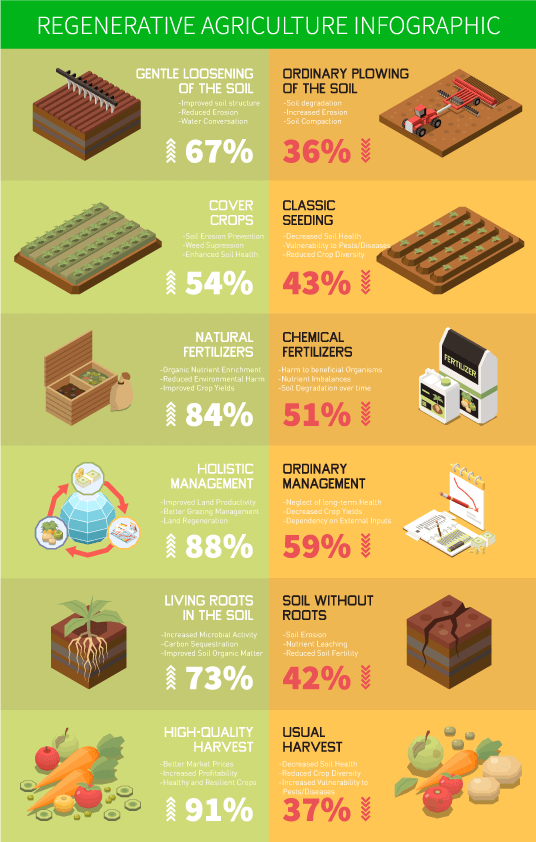
Imagine vast farmlands alive with vibrant ecosystems, teeming with life and vitality. Regenerative Agriculture holds the potential to turn this vision into reality:
Erosion Control: Visualize landscapes where fertile soil remains steadfast, anchored by cover crops and thoughtful land management. Regenerative practices like cover cropping and reduced tillage combat soil erosion, preserving precious topsoil for bountiful harvests. In Zambia, for instance, farmers are implementing contour planting and agroforestry to prevent erosion on sloped terrains, thus safeguarding their land’s productivity.
Enhanced Biodiversity: Picture fields abuzz with pollinators, birdsong filling the air. By nurturing diverse habitats and avoiding monoculture, Regenerative Agriculture invites beneficial insects and wildlife, creating a harmonious balance within ecosystems. South African farmers are planting native flowering plants alongside their crops to attract pollinators and natural predators, promoting biodiversity and reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Soil Health Revival: Envision soils teeming with microbial life, akin to a bustling city underfoot. Practices like composting, crop rotation, and agroforestry restore soil health, boosting nutrient content and water retention. In Kenya, smallholder farmers are adopting vermiculture, using earthworms to create nutrient-rich vermicompost that rejuvenates their soils and enhances plant growth.
Climate Resilience: Imagine farming landscapes that embrace climate fluctuations. Regenerative practices, such as agroforestry and water management, mitigate the impact of extreme weather events, ensuring continuity in agriculture. In Ethiopia, integrated watershed management techniques are being employed to manage water resources, preventing soil erosion and securing water availability for crops during both rainy and dry seasons.
Empowering Farmers: Cultivating Prosperity
Regenerative Agriculture isn’t just about nurturing the land; it’s about uplifting the very farmers who tend to it:
Reduced Input Costs: Visualize farmers liberated from the burden of costly chemical inputs. By promoting natural processes, Regenerative Agriculture reduces dependency on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. In Uganda, farmers practicing agroecology have reported lower production costs as they rely on locally available organic materials for pest control and soil enrichment.
Increased Resilience: Imagine farmers with diversified income streams. Regenerative practices like intercropping and livestock integration create resilient systems that offer multiple revenue sources. Nigerian farmers are integrating poultry and fish farming into their crop production, creating a symbiotic relationship where animal waste enriches the soil while providing additional income.
Improved Livelihoods: Envision thriving farming communities, where incomes are bolstered through value-added products. Regenerative practices open doors to agro-processing and niche markets, elevating farmers’ economic standing. In Ghana, women farmers are processing fruits into jams and dried snacks, adding value to their produce and accessing higher-margin markets.
Strengthened Food Security: Picture communities where access to nutritious food is a certainty. By enhancing soil fertility and crop diversity, Regenerative Agriculture fortifies food security, nourishing populations sustainably. Zimbabwean farmers are practicing crop rotation with leguminous plants like beans and peas, which not only enrich the soil but also provide protein-rich food for local consumption.
Practical Steps: Embarking on the Regenerative Journey
To embrace Regenerative Agriculture is to embark on a transformative journey. Here are practices that African farmers can start with:
Cover Cropping: Visualize fields adorned with a tapestry of cover crops. Planting cover crops between main crops prevents soil erosion, suppresses weeds, and improves soil structure. In Senegal, farmers are using cowpea as a cover crop to enhance soil fertility while conserving moisture.
Agroforestry: Imagine integrating trees within farming landscapes. Agroforestry restores degraded land, sequesters carbon, and offers a myriad of products from fruits to timber. In Malawi, farmers are planting fruit trees alongside their crops, creating shade and enhancing biodiversity while generating additional income from fruit sales.
Composting: Picture nutrient-rich compost enriching the soil. Composting agricultural residues and organic matter recycles nutrients, reduces waste, and enhances soil fertility. Tanzanian farmers are composting crop residues, livestock manure, and kitchen waste to create a nutrient-dense compost that revitalizes their soils.
Crop Rotation: Envision fields rotating with diverse crops. Crop rotation breaks pest and disease cycles, maintains soil health, and optimizes nutrient utilization. Kenyan farmers are practicing crop rotation by alternating maize with legumes like beans, benefiting from improved soil structure and reduced pest pressure.
Holistic Grazing: Imagine livestock grazing on carefully managed pastures. Holistic grazing mimics natural herbivore patterns, regenerating grasslands and improving soil health. South African ranchers are employing rotational grazing, moving livestock through different paddocks to prevent overgrazing and encourage grass growth.
In Conclusion: A Resilient Future Beckons
Regenerative Agriculture is more than a practice; it’s a philosophy that envisions an interconnected world where nature and agriculture coexist harmoniously. By embracing this approach, Africa’s farmers can reap the benefits of sustainable yields, restored landscapes, and empowered communities. It’s a transformative path that beckons us towards a resilient future, where the land flourishes, livelihoods thrive, and generations to come inherit a legacy of nurturing rather than exploiting the Earth. As the sunflowers turn their faces to the sky, they remind us of the enduring connection between nature and artistry, a connection that defines the essence of sunflower farming.
Stay updated with the latest farming tips and agriculture industry news from Africa by subscribing to our newsletter. Don’t miss out on valuable insights and updates. Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook to join our farming community and stay connected with us.



















