
Organic farming and regenerative farming are two approaches to sustainable agriculture that share some common goals, but differ in their methods and philosophies. In this article, Organil Services compares and contrast these two farming practices, highlighting their benefits and challenges.

Organic farming is a system of agriculture that avoids the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).

It aims to promote soil and water quality, biodiversity, and human health by following a set of standards and regulations. Organic farming has been growing in popularity and demand, as consumers seek more natural and healthy food options. However, organic farming also faces some limitations, such as higher costs, lower yields, and potential nutrient deficiencies.

Regenerative farming is a process of restoring degraded soils using practices based on ecological principles.
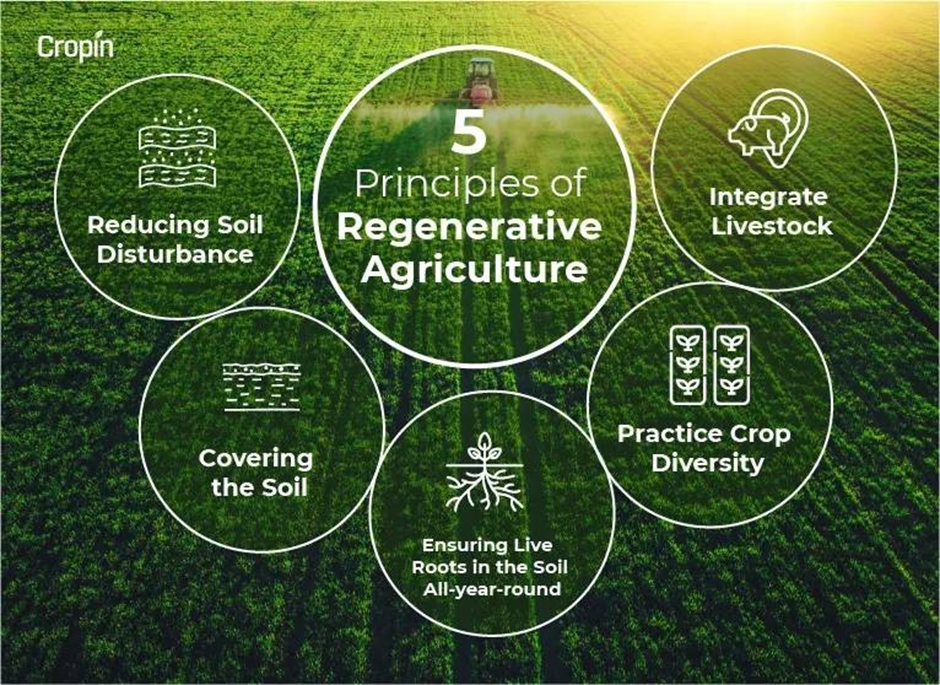
It goes beyond organic farming by not only avoiding synthetic inputs, but also actively enhancing the natural ecosystems of the land. Regenerative farming seeks to improve soil health, carbon sequestration, water retention, and biodiversity by employing techniques such as cover cropping, crop rotation, no-till farming, agroforestry, and livestock integration. Regenerative farming has the potential to mitigate climate change, improve food security, and support rural livelihoods. However, regenerative farming also faces some challenges, such as lack of awareness, incentives, and research.
Some of the challenges that farmers may face when choosing between organic and regenerative farming are:
– Organic farming requires following a set of standards and regulations, which may limit the flexibility and adaptability of the farmers. Regenerative farming is more based on principles and outcomes, which may allow more room for innovation and experimentation.
– Organic farming may not address the holistic aspects of the ecosystem, such as soil health, water retention, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity. Regenerative farming considers the interactions among the soil, water, plants, animals, and humans, and aims to enhance the natural ecosystems of the land.
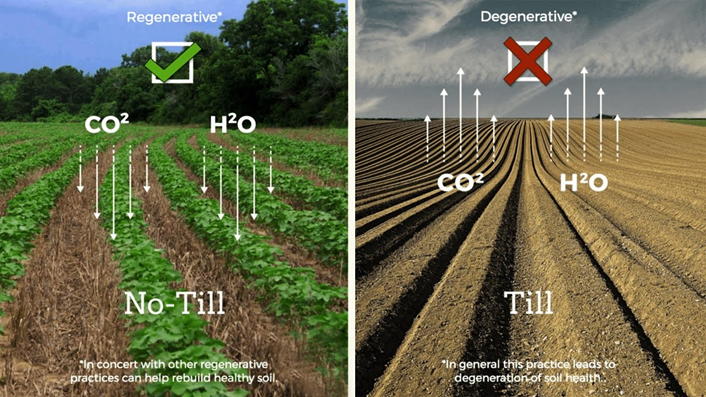
– Organic farming may use tillage methods that disrupt the soil structure and cause erosion. Regenerative farming minimizes soil disturbance and erosion by using techniques such as cover cropping, crop rotation, no-till farming, and agroforestry.
– Organic farming may face higher costs, lower yields, and potential nutrient deficiencies, especially in the initial transition phase. Regenerative farming may improve soil fertility, crop productivity, and profitability in the long term, but it may also require initial investments in new equipment, training, and alternative farming techniques.
– Organic farming may have more market access and demand, due to consumer preferences and existing supply chain structures. Regenerative farming may face challenges in accessing mainstream markets, due to lack of awareness, labelling, and certification.
These challenges are not insurmountable, and both approaches can learn from each other and complement each other, depending on the context and objectives of the farmers and consumers. However, they do require careful consideration and planning before making a decision.
Main differences between organic and regenerative farming:
Organic Farming
- Focuses on avoiding synthetic inputs
- Follows a set of standards and regulations
- Contributes to reduced carbon emissions
- May use tillage methods that disrupt soil structure
- May not address the holistic aspects of the ecosystem
Regenerative Farming
- Focuses on enhancing natural ecosystems
- Adapts to site-specific conditions and goals
- Contributes to increased carbon sequestration
- Minimizes soil disturbance and erosion
- Considers the interactions among soil, water, plants, animals, and humans
Exploring the distinctions between organic and regenerative farming is essential for staying abreast of evolving agricultural practices. Both methodologies contribute significantly to sustainable and environmentally conscious farming, but understanding their unique characteristics empowers farmers to make informed choices based on their specific needs and local conditions. Embracing the synergies between these approaches could pave the way for a more resilient and ecologically harmonious agricultural future.
Anil M V, Founder, Organil Services

Organil Services are Registered for Organic Regulatory Certification Consultancy and Accreditation Services in the Industry. WhatsApp for a Prepaid Consultancy +91 8606551335 or Email : orgnil40@gmail.com


















